Broadband vs Wi-Fi: Which One Truly Speeds Up Your Life?
Published: 28 Aug 2025
Did you know that more than half of internet users confuse Broadband vs Wi-Fi? Many people believe Wi-Fi is the internet itself, but that’s not the case. Broadband is the primary means of bringing the internet to your home. Wi-Fi is just the wireless way to share that pipeline with your devices. When you mix the two up, it becomes harder to solve problems like slow speed or buffering. By learning the simple difference, you’ll know whether to check your broadband plan or adjust your Wi-Fi router first. This knowledge can save you time, money, and a lot of frustration.
What is Broadband?
Broadband refers to a high-speed internet connection delivered through different technologies such as fiber optic, DSL, cable, or satellite. It is the backbone of your internet access and provides the actual data connection from your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Speed & Stability: Broadband is usually faster and more stable compared to older dial-up connections.
Types of Broadband
Here are some important types of broadband.
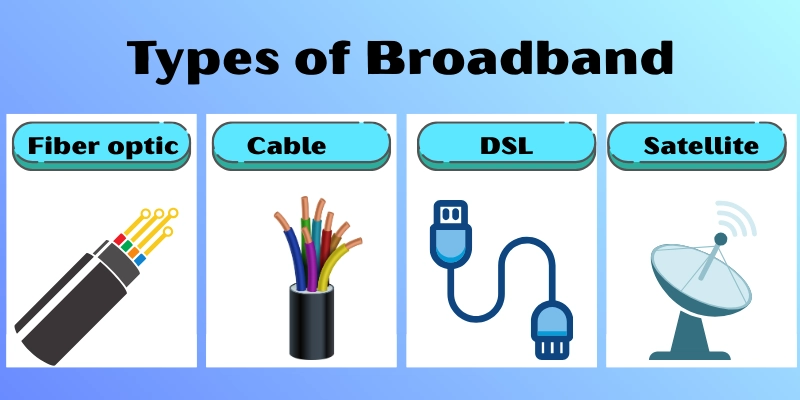
- Fiber optic – fastest and most reliable.
- Cable – widely available with decent speeds.
- DSL – affordable but slower.
- Satellite – available in remote areas but may face latency issues.
In short, broadband is the source of internet access.
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi, on the other hand, is not the internet itself but a wireless technology that allows devices to connect to broadband without physical cables.
- A router takes the broadband connection and broadcasts it wirelessly.
- Devices such as laptops, smartphones, smart TVs, and tablets can then connect within the Wi-Fi range.
- The speed and performance of Wi-Fi depend on the router quality, distance, and interference.
Simply put, Wi-Fi is the way you access broadband wirelessly.
Broadband vs Wi-Fi: Key Differences
Broadband gives you internet access, while Wi-Fi lets you use it wirelessly across devices. Here are some differences between broadband and wi-fi.
| Feature | Broadband | Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Wired (fiber, cable, DSL, satellite) | Wireless (via router) |
| Speed | Raw speed from ISP | Limited by the provider’s infrastructure |
| Reliability | Stable, less interference | Can drop with distance or walls |
| Coverage | Limited by provider’s infrastructure | Limited by router range |
| Security | Safer when wired | Limited by the provider’s infrastructure |
Broadband Pros and Cons
Speed and dependability are good things about broadband, but it also has some problems.
| Advantages of Broadband |
|---|
Let’s see some important pros of broadband.
|
| Disadvantages of Broadband |
|---|
Let’s see the importance cons of broadband.
|
Wi-Fi Pros and Cons
Although Wi-Fi increases mobility and convenience, it may not be as fast or secure.
| Advantages of Wi-Fi |
|---|
Let’s see some important pros of Wi-Fi.
|
| Disadvantages of Wi-Fi |
|---|
Let’s see some important cons of Wi-Fi.
|
Broadband vs Wi-Fi for Different Needs
Choosing between Broadband vs Wi-Fi depends on how you use the internet and what your needs are.
- Home users: Broadband gives you speed, and Wi-Fi makes it easier to connect multiple devices.
- Gamers: Wired broadband has lower latency than Wi-Fi, which could lead to lag.
- Businesses: Broadband makes sure things stay stable, and Wi-Fi lets workers move around.
- Students: Wi-Fi gives you more options, but you need fast broadband for online classes.
- Rural areas: Broadband may not be available everywhere, so satellite Wi-Fi may be needed.
Which One Should You Choose?
You frequently need both, so it’s not always a matter of picking between Broadband vs Wi-Fi. Broadband gives you a strong, fast, and stable internet connection, perfect for gaming, streaming, or working. By enabling wireless connections between numerous devices anywhere in your house, Wi-Fi increases convenience.

- Therefore, choose broadband for speed and stability.
- Select Wi-Fi for comfort and flexibility.
- The best choice? For the greatest internet experience, combine the two.
Conclusion
Although they have different functions, Broadband vs Wi-Fi are frequently confused. Wi-Fi is a wireless method of accessing the internet, whereas broadband is the actual internet service. Wi-Fi offers you convenience and freedom, while broadband offers speed, stability, and dependability. While Wi-Fi allows for flexibility and mobility in homes and offices, broadband is necessary for tasks like online gaming, large downloads, and business use. Both technologies are essential for using the internet today because they enhance one another. For optimal performance, coverage, and convenience, the ideal configuration combines broadband with a powerful Wi-Fi router.
FAQs
Here are some important FAQs related to Broadband vs Wi-Fi. Let’s get started.
Broadband Internet refers to high-speed Internet access, often compared to traditional dial-up access. This includes various techniques such as DSL, cable, fiber optic, and satellite services.
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technique that allows devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, to connect to the Internet through radio waves. It usually requires a broadband Internet connection to transfer data.
Broadband is the technique that provides internet access, while Wi-Fi is a method of connecting the unit to the Internet provided by a broadband service.
Yes, you need a broadband connection to deliver internet access, which then distributes your equipment wirelessly.
Broadband can offer high speed (depending on the type, such as fiber is faster than DSL), but the speed of Wi-Fi may vary depending on the strength of the signal, distance from the router, and the interference from other equipment.
Wi-Fi requires a broadband connection to access the Internet, although you can use Wi-Fi for local network purposes without Internet access.
If you use a strong password, you activate network encryption (WPA3 or WPA2) and update regular firmware.
You can improve the Wi-Fi signal by placing the router in a central location, reducing obstacles, using a Wi-Fi Extender, or upgrading to a new router model.
Yes, you can connect the device directly to a modem or router using Ethernet cables, using Ethernet cables completely bypassing Wi-Fi.
Common types of broadband include DSL, cable, fiber-optic, satellite, and fixed wireless.
Mobile data is a type of wireless internet access provided by a cellular network, while broadband usually refers to fixed high-speed services. They are equal to providing internet use, but are different in distribution and technology.
Consider factors like speed requirements, availability in your area, budget, customer service, and data limits when choosing a broadband service.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks