Complete History of the Internet Timeline: Important Events Explained
Published: 17 Sep 2025
From a simple research project to a global network connecting billions, the history of the internet timeline is full of exciting milestones. Imagine a time when it was a success to send a simple message between two computers, how it all started. Over the decades, scientists, engineers, and dreamers have experimented in today’s powerful online world. How did we transition from curious machines to lightning-fast connections and social media?

Let’s take a walk through the fascinating history of the internet timeline and see how it shapes our way of living, working, and sharing information.
Brief Internet History
In the late 1960s, the Internet began as a project from the US government, called ARPANET, which involved connecting research computers to share data. In the 1980s, the network expanded and began to utilize TCP/IP, the system that still connects computers. The launch of the World Wide Web in the early 1990s made sites and browsers more common. From dialing connections to today’s high-speed broadband and mobile internet, it has developed into a large-scale global network that we all use for work, learning, and entertainment.
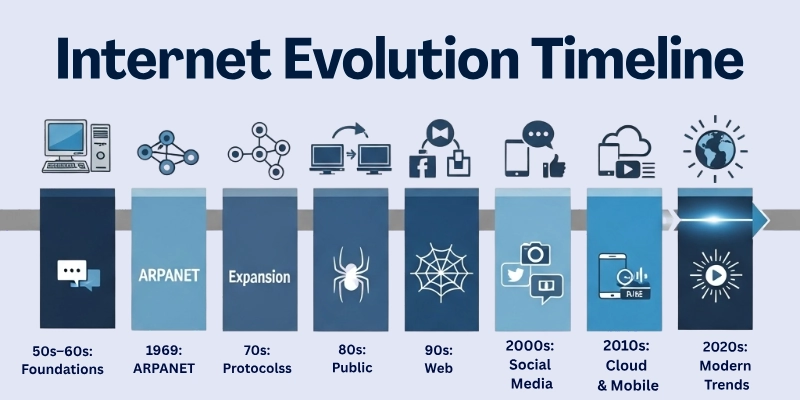
History of the Internet Timeline: Major Developments
Internet Story is a journey with smart ideas and direct progress. From the first experiments of connecting the computer to today’s super-fast 5G network, each step changed how people share information and communicate. Here is a clear time for the most important successes that the web is used every day.
- Early Foundations (1950s–1960s)
- Birth of ARPANET (1969)
- Expansion and Key Protocols (1970s)
- From Research to Public Use (1980s)
- Birth of the World Wide Web (1990s)
- Broadband and Social Media Boom (2000s)
- Cloud, Mobile, and Streaming Era (2010s)
- Modern Internet Trends (2020s and Beyond)
1. Early Foundations (1950s–1960s)
Internet roots began in the 1950s and 1960s when researchers discovered ways of sharing information for computers. This period determined the phase of modern networks.
- Researchers studied how they can add computers to quick communication.
- A method was created to cut information into small bits so it could travel quickly.
- ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) funded the first network research.
- The user focused on connecting government and university computers.
- The first projects proved that computers could “talk” to each other over long distances.
- These findings first created the basis for large computer networks.
- Tip: Data exchange is still the main idea behind today’s data transfer on the Internet.
2. Birth of ARPANET (1969)
In 1969, a great milestone, came the first real computer network with the construction of the Arpanet. It is connected to universities and researchers so that they can quickly share data and collaborate.
- Four main universities were added to the United States.
- Two computers (the word “login” sent the first message between the word “login”, even though it crashed after “low”).
- Showed that long-distance communication was possible.
- Funded by the U.S. Defense Department’s ARPA program.
- Became the foundation for the modern Internet.
- Inspired other countries and researchers to build their own networks.
- Tip: ARPANET proved that computers can communicate FAST, which created today’s global internet.
3. Expansion and Key Protocols (1970s)
During the 1970s, the Internet expanded beyond the same network. Researchers worked in ways to connect many small networks so that they could easily share information.
- Developed TCP/IP, the main set of rules for sending and receiving data.
- The idea of an “Internet” network made by several connected networks was introduced.
- Several universities and public agencies joined these networks.
- This allowed people to share research quickly in different places.
- Help a variety of computers that work together without any problems.
- Today, we set a platform for the internet all over the world.
- Tip: TCP/IP is still the basic language of the Internet even after decades of development.
4. From Research to Public Use (1980s)
In the 1980s, the Internet began to move from research laboratories to the public. New equipment and services made it easier to get everyday people and businesses online.
- The Domain Name System (DNS) was introduced to replace long computer numbers with simple names such as “Example.com”.
- The first commercial Internet service providers (ISPs) offered access to the Internet.
- Email and early online communities became popular for sharing messages.
- More schools and companies began connecting their com
- The network increased beyond the authorities and university research.
- This round opened the door to reach homes and businesses all over the world for the Internet.
- Tip: DNS is like an Internet Phone Book, which makes it easy to find websites without remembering the numbers.
5. Birth of the World Wide Web (1990s)
The World Wide Web was launched in the 1990s, making it simple for anyone to use the Internet. This system was created by Tim Berners-Lee to allow users to view and share information via basic web pages.
- The first website was made by Tim Berners-Lee, who also invented the Web.
- Web pages were easy to open and read with early web browsers.
- Websites covering businesses, hobbies, and news quickly expanded.
- E-commerce and online shopping first emerged.
- The Web made the Internet accessible to non-researchers as well.
- The contemporary online experience as we know it today began in this decade.
- Tip: We are able to browse pages and click links instead of just sending text messages because of the World Wide Web.
6. Broadband and Social Media Boom (2000s)
In the 2000s, rapid connections and new ways came to connect people online. High-speed internet changed how quickly we can browse, watch videos, and share information.
- Broadband replaced slow dial-up, making streaming and large downloads possible.
- Social media platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter became popular around the world.
- People started sharing photos, videos, and personal updates every day.
- Mobile phones and preliminary smartphones let users go anywhere online.
- Online communications were transferred from email to instant messaging and social networks.
- Companies began to use social media for marketing and customer service.
- Tip: Broadband made the internet quickly and more interactive, establishing the platform for today’s mobile and video-driven world.
7. Cloud, Mobile, and Streaming Era (2010s)
The 2010s changed how people work, see, and share material. Shooting technology, smartphones, and streaming have reshaped everyday life around the world.
- Cloud computing allows users to save files and run online apps without powerful hardware.
- Smartphones and mobile apps made it easy to stay anywhere, anytime.
- Video streaming platforms such as Netflix, YouTube, and Twitch exploded in popularity.
- On-demand content replaced traditional TV schedules.
- Apps on social media grow rapidly with mobile-first designs.
- Companies were transferred to a cloud-based tool for distance work and teamwork.
- Tip: Cloud services and mobile apps converted the Internet into a “carrying care” tool for work, fun, and communication.
8. Modern Internet Trends (2020s and Beyond)
In the 2020s, the Internet continues to grow and develop, providing rapid connections and smart technology. New equipment and services shape how we live, work, and remain safe online.
- The 5G networks offer power speed for power and better global connection.
- Internet of Things (IoT) links to smart devices such as home assistants and wearables.
- Focus strongly on privacy and data security for users’ security.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) Power Smart Search, Chatbots, and Personal Services.
- Remote work and online learning are still the most important parts of daily life.
- Virtual and improved reality creates new ways of detecting networks.
- Tip: It is important to be aware of privacy settings and security updates as the Internet becomes more connected and intelligent.
Key Milestones Recap
Here is a short history of the internet timeline for the most important internet successes and how each step changed us to connect:
- The 1950s -1960s: Initial research created new ways of sharing data for computers, which made the basis for networks.
- 1969: ARPANET added many US universities and sent the first computer-to-computer message.
- The 1970s: TCP/IP protocol added many small networks to a large “internet”.
- The 1980s: Domain Name System (DNS) and the first Internet providers opened access beyond research laboratories.
- The 1990s: Tim Burner-Li created the World Wide Web, which led to a boom in websites and online shopping.
- The 2000s: Broadband and an increase in social media platforms changed communication and entertainment.
- 2010s: Cloud computing, smartphones, and video streaming became part of everyday life.
- 2020 and beyond: 5G networks, smart home units, and AI-operated equipment form the future of the Internet.
Conclusion
So guys, in this article, we’ve covered the history of the internet timeline in detail. From the first computer connection in the 1950s to 5G and AI in today’s world, every milestone shows where rapid human creativity can change our way of life. My personal advice: Continue to search the Internet to understand how new trends will shape her future, and always be careful about privacy and data security online. Share this post with friends and join the conversation; you can help shape the next exciting chapter in internet history.
FAQs
Check out these FAQs on the History of the Internet Timeline to understand how the internet started and where it’s heading.
It’s a record of the main events that shaped the internet from its early experiments to today’s worldwide network. It highlights big steps such as ARPANET, the World Wide Web, and social media. This timeline shows how the internet grew into a tool billions of people use every day.
The first version began in 1969 with ARPANET, created by the U.S. Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). It allowed universities and researchers to share data quickly. ARPANET became the base for the modern Internet.
Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web in 1989 while working at CERN. He designed it to make sharing and accessing information easier. This invention introduced websites, browsers, and hyperlinks.
In the 1980s, commercial internet service providers (ISPs) allowed people outside universities and government offices to connect. The Domain Name System (DNS) made websites easier to find. These changes helped the internet reach homes and businesses.
Packet-switching is a way of breaking data into small packets so it can travel across networks quickly and reliably. This ensures messages can be delivered even if some paths are busy or broken. It’s still the backbone of internet communication today.
Key milestones include the launch of ARPANET (1969), the creation of TCP/IP protocols (1970s), the invention of the World Wide Web (1990s), the rise of social media (2000s), and the growth of cloud computing and 5G networks (2010s–2020s).
Platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter in the 2000s turned the internet into a place for sharing and real-time communication. They made it easy for anyone to post and connect. This transformed online interaction around the world.
Smartphones and tablets brought the internet into people’s hands during the late 2000s and 2010s. Mobile apps and fast networks allowed users to browse, shop, and stream anytime. This made internet access more personal and constant.
Knowing this history explains how today’s technology evolved and affects our daily lives. It shows how innovators overcame challenges like slow speeds and limited access. Understanding the past also helps us prepare for future digital changes.
The future includes faster 5G and beyond, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) linking smart devices everywhere. Privacy and security will remain major concerns. These trends will keep shaping how we work, communicate, and live.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks