Information Security Explained: Risks, Types, and Benefits
Published: 12 Sep 2025
Every 39 seconds, a hacker strikes somewhere in the world, resulting in more than 2,200 cyberattacks every day. The big question is, how safe is your personal or business information? Many people believe that a strong password is sufficient, but information security is more complex. It protects data, systems, and networks from hackers, fraud, and unauthorized access. Without strong security, business customers take the risk of losing confidence, while individuals face dangers such as identity theft and financial losses.

Simply put, information is the basis for information security Digital Trust, which is a need, not just one option, in today’s connected world.
📘 What is Information Security?
Information security is the practice of protecting data from theft, loss, or unauthorized access and use. This ensures that your personal and business information remains private, accurate, and accessible only to intended persons.
Many confuse information security with cybersecurity. The difference is simple:
- Information security is widespread. It protects both physical information (such as files or documents) and digital data.
- Cybersecurity information is one of the most important forms of aspects of information protection, focusing primarily on the security of systems, networks, and online data against hackers.
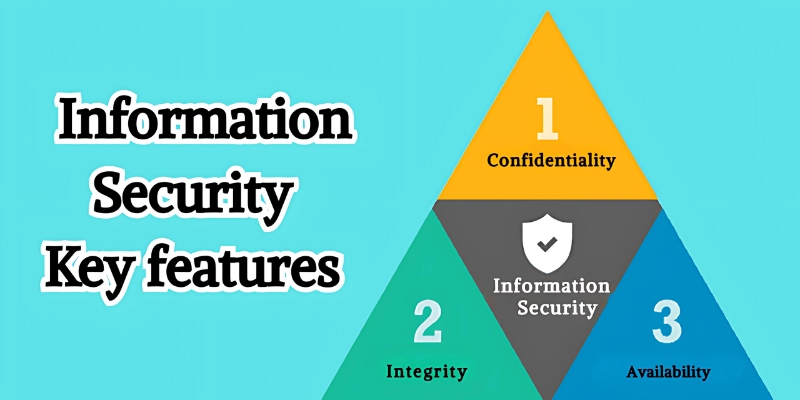
🔑 Key Principles of Information Security (CIA Triad)
The basis for information security rests on three main principles, known as the CIA Triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These principles work together to keep data safe and reliable.
1. Privacy (Confidentiality)
Privacy is about keeping information safe and only accessible to people who are allowed to see it. It prevents sensitive data from being stolen, shared, or misused. This is important for personal accounts, business records, and online transactions.
- Use strong passwords for accounts.
- Encrypt sensitive data.
- Limit access to only those who need it.
- Avoid sharing personal information online carelessly.
- Monitor accounts for suspicious activity.
2. Integrity
Integrity ensures that data remains correct, complete, and unchanged by unauthorized users. It makes sure that information is trustworthy and reliable for decision-making. Without integrity, mistakes or tampering can cause big problems for individuals and organizations.
- Use secure databases and systems.
- Implement access controls for editing data.
- Regularly check and verify records.
- Track changes to detect errors or tampering.
- Protect systems against malware that can modify data.
3. Availability
Availability makes sure that information is always ready and accessible when needed. It ensures systems, websites, and data are up and running without interruption. This is crucial for businesses, online services, and emergencies where timely access is required.
- Keep servers and websites running 24/7.
- Use backup systems for emergencies.
- Monitor system uptime and performance.
- Ensure cloud services are reliable.
- Prepare disaster recovery plans for quick access.
Together, these three principles make up the backbone of safe and reliable information systems.
⚠️ Common Threats in Information Security
Information faces many dangers in today’s digital world. Some come from hackers outside, while others may even come from trusted people inside an organization. Knowing these threats helps you prepare better.
1. Malware and Viruses
These are harmful programs designed to disrupt the system or steal data.
- Download fake software or spread through an infected USB.
- Damage files and slow down the computer.
- Permanent data can cause loss.
- Example: A virus enters the laptop after installing pirated software.
2. Phishing Attacks
Phishing tricks for users with fake messages that look real.
- Often targeting bank accounts, credit cards, or passwords.
- Emails and texts usually look official.
- If you are not awake, it is easy to fall.
- Example: An email that pretends to be from your bank asks you to “confirm your account”.
3. Insider Threats
These dangers come from employees or reliable users in a company.
- Intentional (stealing data) or random (careless actions) may be.
- It is often more difficult to detect than attacks outside.
- Companies can suffer serious losses.
- Example: An employee mimics secret company files to sell membership to competitors.
4. Ransomware
Ransomware locks files and requires money to unlock them.
- Generally, businesses and hospitals are targeted.
- Attackers cannot regain access even after payment.
- Heavy damage and shutdown lead to.
- Example: Hospitals cannot access the records until they pay the attackers.
5. Data violation
A data violation occurs when sensitive information is revealed or stolen.
- Due to a weak password, poor security, or an online attack.
- Financial loss and loss of confidence lead to losses.
- Affects both businesses and customers.
- Example: An e-commerce site is leaking millions of credit card details.
6. Social Engineering
Social engineering manipulates people into giving away private details.
- Attackers use trust and psychology instead of technical hacking.
- It can happen over phone calls, emails, or in person.
- Often used as the first step in bigger attacks.
- Example: A caller pretending to be IT support asking for your password.
💼 Importance of Information Security for Businesses
For companies, not only is information protection about data protection, it is about protecting survival and development. A simple cyber attack can damage trust, cause heavy losses, and even shut down operations. This is why strong security is necessary for any organization.
- Protecting customer trust: Customers share safe data when they know it is safe.
- Avoid financial losses: Hack prevents expensive damage from cheating or a shutdown.
- Meeting compliance regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, ISO): Helps companies to remain legal and avoid penalties.
- Ensuring smooth business operations: Prevents disorders that slow down work or services.
- Building long-term brand reputation: The company, known for security, attracts more loyal customers.
- Prevention of data violations: Strong security measures or reduce the possibility of theft.
- Protection of intellectual property: Protects business secrets, strategies, and innovations.
- Support Business Development: Safety gives confidence in scaling into new markets.
🔐 Types of Information Security
Information security has many layers, and each one focuses on protecting data in a different way. From securing networks to training employees, every type plays a role in keeping information safe and trustworthy.
- Network Security: Protects data while it moves across networks.
- Application Security: Fixes vulnerabilities in apps and software.
- Cloud Security: Keeps online-stored data safe from leaks and hacks.
- Physical Security: Controls access to servers, devices, and hardware.
- Operational Security: Ensures policies and procedures are followed.
- Endpoint Security: Protects laptops, phones, and other end-user devices.
- Data Security: Protects stored information with encryption and backups.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM): Makes sure only authorized users can access systems.
- Mobile Security: Secures smartphones, tablets, and mobile apps from threats.
- Disaster Recovery & Business Continuity: Ensures data and systems can be restored after an attack or failure.
🛡️ Best Practices for Strong Information Security
Good security begins with smart habits. Both individuals and companies can reduce the risk of following some simple but powerful practices.
- Use a strong password, create multifactor authentication and other passwords, and add an extra login phase, such as SMS or app code.
- Keep software updated: Fix update problems and close security holes that hackers could use to steal your data.
- Train employees and raise awareness: Teach staff to spot phishing emails, scams, and risky behavior.
- Encrypt sensitive data: Protect important files and messages so that only the right people can read them.
- Revision Regular Security: Often check the system to find and fix weak points before the attackers do.
- Use antivirus and firewall: Add more shields to block malware and suspicious activity.
- Limit access rights: Only give people access to data that they actually need.
- Regular data backups: Save copies safely so you can restore information after an attack or failure.
🛡️Information Security vs Cybersecurity💾
This table shows the main differences between Information Security and Cybersecurity in a simple way.
| Feature | Information Security | Cybersecurity |
| Definition | Encrypting files, locking server rooms, and managing access. | Focuses only on protecting data in digital form. |
| Main Focus | Confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. | Defending networks, devices, and systems from attacks. |
| Scope | Broad includes policies, physical security, and digital security. | Encrypting files, locking server rooms, and managing access. |
| Examples | Encrypting files, locking server rooms, managing access. | Firewalls, antivirus, phishing protection, threat monitoring. |
| Why It Matters | Builds trust and keeps all data safe. | Stops hackers, malware, and online threats in real-time. |
✅Real-Life Examples of Information Security
Information security is everywhere around us, protecting data, people, and businesses. Here are some real-world cases:
- Banking: A bank uses multi-factor authentication (MFA) so hackers can’t break into accounts with just a stolen password.
- Healthcare: Hospitals encrypt patient records and limit access so only authorized doctors can view them.
- Startups: Small businesses use cloud security to keep client data safe from leaks or hackers.
- E-commerce: Online stores secure credit card payments with SSL certificates and fraud detection tools.
- Education: Schools protect student data by using secure learning platforms and strict login controls.
- Government: Agencies use firewalls, encryption, and monitoring systems to safeguard sensitive national data.
📝Conclusion
So, guys, in this article, we’ve covered Information Security in detail, what it is, why it matters, common threats, and best practices. My recommendation is to start small: use strong passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, and keep your software updated. But be careful, many people make the mistake of ignoring employee training or thinking “it won’t happen to me.”
👉 Begin securing your data today, because the earlier you act, the safer you’ll be. Remember: protecting information means protecting your future.
❓ FAQs: Information Security
Here are some FAQs about Information Security to help you understand the basics and avoid confusion.
Information security means protecting your data, like emails, bank details, or company files, from hackers, leaks, or misuse. It covers both digital and physical protection. Think of it as locking your doors, but for your data.
Information security is a broad term that covers protecting all types of information, both digital and physical. Cybersecurity is a part of it and focuses only on online and digital threats. In short, all cybersecurity is information security, but not all information security is cybersecurity.
Small businesses are often easy targets for hackers because they lack strong defenses. A single attack can cause financial loss or loss of customer trust. Good security builds credibility and keeps your business running smoothly.
The most common ones are phishing emails, ransomware, malware, insider misuse, and data breaches. These can steal, damage, or lock your data. Staying aware of these threats is the first step to protection.
Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA). Keep your software and devices updated. Avoid clicking on suspicious links or emails.
CIA stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Confidentiality means keeping data private, Integrity means keeping data accurate, and Availability means making sure it’s always accessible when needed. These three are the foundation of all security practices.
Yes, cloud storage can be safe if you choose a trusted provider and use extra measures like encryption and MFA. However, weak passwords or poor settings can still expose your data. Always double-check your security setup.
Act fast, disconnect affected systems, inform stakeholders, and follow your incident response plan. Change passwords, fix the vulnerability, and report it if legally required. Delaying action makes the damage worse.
The main goal is to protect data from being stolen, misused, or damaged. It ensures your information stays private, accurate, and available when needed. In simple words, it’s about keeping your data safe and trustworthy.
The 4 common types of security are:
- Network Security: Protecting data while it travels across networks.
- Application Security: Keeping apps safe from bugs and attacks.
- Cloud Security: Protect data stored in the cloud.
- Physical Security: Protecting servers, computers, and devices from theft or damage.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks