What is LAN Topology? Types, Examples, and Easy Beginner Guide
Published: 3 Sep 2025
Slow network? Your LAN topology could be the reason. Learn how to choose the right setup for speed, reliability, and easy troubleshooting. Some networks run fine, while others are slow or keep cutting out. Picking the right LAN topology can make your network faster, more reliable, and easier to fix. In this guide, you’ll learn the main types, their pros and cons, and real-life examples to help you choose the best setup.
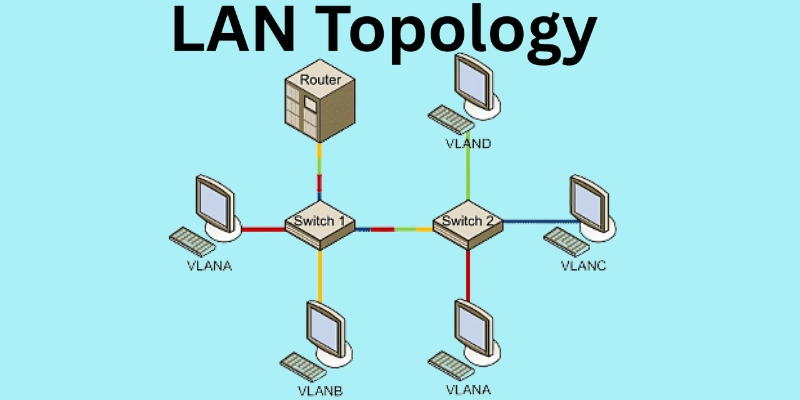
What is LAN Topology
LAN topology refers to the method by which computers and devices are connected in a local area network. It shows how data moves between devices and how the network is organized.
Why LAN Topology is Important
LAN topology is important because it determines how devices are connected and communicate within a network. The right topology makes the network faster, more reliable, and easier to fix. It also helps to reduce problems such as slow speed, disconnection, and high costs. In short, LAN topologies affect the performance, stability, and development of any network.
Types of LAN Topologies
There are different types of LAN topologies, such as:
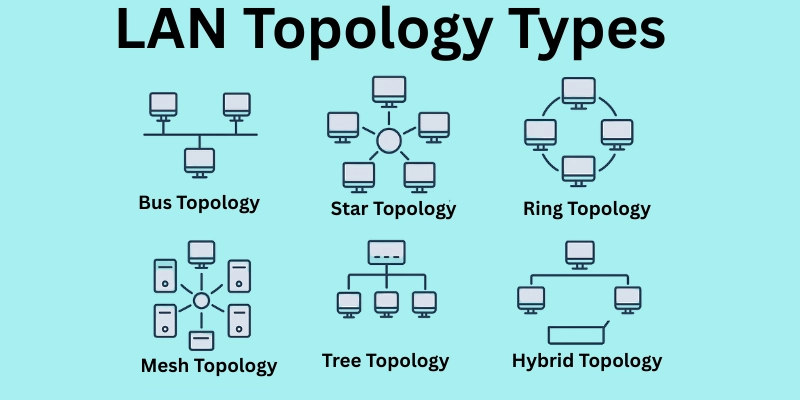
- Hybrid Topology
- Bus Topology
- Star Topology
- Ring Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Tree Topology
1. Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology is a mix of two or more different topologies, making it highly flexible. It is commonly used in large and complex organizations for better performance and management.
How it Works: It connects networks using various topologies (such as star, bus, or mesh) within a single system. Data travels according to the rules of each combined topology, ensuring smooth communication.
Advantages: It is highly scalable and supports network growth without issues. It offers flexibility to design according to organizational needs.
Disadvantages: Installation is expensive, and managing multiple topologies can be difficult.
2. Bus Topology
It is one of the oldest and simplest network designs. It connects all devices to a single central cable, called a bus topology.
How it works: Data travels with a central cable, and all devices share the same cable. Only one device can send data at once.
Benefits: It is easier to install and makes it cheaper than other topologies. Works well for small networks with limited equipment.
Disadvantages: If the main cable breaks, the entire network stops. As several tools are added, the performance slows.
3. Star Topology
This is the most widely used LAN topology today. It is common in offices, schools, and home networks.
How it works: Each device is connected directly to a central hub or switch. The hub manages and controls data flow.
Benefits: It is very reliable because if one device fails, others still work. It is very reliable, and you can add or remove devices without affecting the network.
Disadvantages: If the hub or switch fails, the entire network goes down. More cables are required than bus topology.
4. Ring topology
This topology arranges devices in a circular loop. The data travels around the ring in a particular direction.
How it works: Each device is connected to two other devices and forms a circle. The data goes through each device until it reaches the target.
Advantages: Provides an organized stream of data with low collisions. It handles data transfer smoothly.
Cons: If a device or connection fails, it can affect the entire ring. It is harder to troubleshoot problems.
5. Mesh Topology
This topology is often used in large and important networks. It provides the highest reliability.
How it works: Each device is connected directly to all other devices. This creates several paths for data transfer.
Advantages: Extremely reliable because one failure won’t stop the network. If a path fails, the data may take another route.
Cons: Expensive because it needs many cables and ports. Complicated to install and manage.
6. Tree Topology
This topology connects the bus and star design. It is usually seen in large companies or universities.
How it works: Groups of star networks are connected by means of a central spine cable. It creates a hierarchical structure.
Pros: It is easy to expand by adding more equipment or groups. Helps manage large networks easily.
Disadvantages: If the spine fails, the entire network is affected. More cabling and careful plans are required.
How to Choose the Right LAN Topology
When choosing a LAN topology, you need to balance size, cost, reliability, and ease of setup.
Size of the Network
The number of devices in a network directly affects which topology works best.
- Small offices or home networks often use a Star topology for simplicity.
- Large organizations may prefer Hybrid or Mesh to handle more devices.
- The bigger the network, the more important scalability becomes.
- Overloading a small topology can cause performance issues.
Budget
Your available budget often limits the type of topology you can choose.
- Bus and Star are cheaper because they require less cabling.
- Mesh and Hybrid are costlier due to extra hardware and wires.
- Low-budget setups usually stick to simple designs.
- More investment usually brings better reliability and performance.
Reliability Needed
The importance of uptime and fault tolerance determines the best option.
- Mesh and Hybrid provide high reliability with backup paths.
- Star is stable, but if the hub fails, the whole network stops.
- Bus and Ring are less reliable due to single cable or point failures.
- Critical systems need topologies that ensure redundancy.
Ease of Setup
Some topologies are simple to install, while others need expertise.
- Star and Bus are the easiest and quickest to set up.
- Mesh requires heavy cabling, making installation complex.
- Hybrid needs planning to combine multiple topologies correctly.
- The harder the setup, the higher the need for skilled technicians.
LAN Topology Common Problems and Solutions
Local Area Network (LAN) topologies often face issues that affect speed, reliability, and scalability. Below are the most common problems in different LAN topologies and practical solutions to fix them.
1. Star Topology Issues
Star networks are reliable but heavily depend on the central hub/switch.
Common Problems:
Here are some common problems.
- Single Point of Failure – Hub failure stops the entire network.
- High Cabling Cost – Needs more cables than Bus or Ring.
- Performance Bottlenecks – Heavy traffic slows down the hub.
- Limited Expansion – Too many devices overload the hub.
Solutions:
Here are some common solutions.
- Use backup hubs or redundant switches.
- Apply structured cabling to cut costs.
- Upgrade to Gigabit/10G switches.
- Use scalable switches or switch stacking.
2. Bus Topology Issues
Bus topology is simple and cost-effective, but struggles with traffic and faults.
Common Problems:
Here are some common problems.
- Data Collisions – Multiple devices sending data at once.
- Difficult Troubleshooting – One faulty node affects all.
- Cable Breakage – A single cut shuts the network.
- Limited Scalability – More devices reduce efficiency.
Solutions:
Here are some common solutions.
- Use CSMA/CD or migrate to Star.
- Test devices individually and segment the bus.
- Regularly inspect and maintain cables.
- Upgrade to a more scalable topology.
3. Ring Topology Issues
Ring provides orderly data flow, but is highly sensitive to breaks.
Common Problems:
Here are some common problems.
- Single Node Failure – One crash breaks the loop.
- Difficult Maintenance – Adding/removing devices is tricky.
- Slower Speeds – Data passes through multiple nodes.
- Troubleshooting Delays – Hard to find exact faults.
Solutions:
Here are some common solutions.
- Use dual-ring systems for backup.
- Schedule updates during low traffic.
- Upgrade hardware for faster speeds.
- Use monitoring tools for quick detection.
4. Mesh Topology Issues
Mesh is reliable but expensive and complex.
Common Problems:
Here are some common problems.
- High Cost – Needs lots of cables and ports.
- Complex Setup – Full connections need advanced skills.
- Maintenance Difficulty – Too many links to manage.
- Space Issues – Excess cabling clutters the space.
Solutions:
Here are some common solutions.
- Use a partial mesh instead of a full mesh.
- Hire professionals for installation.
- Apply network management tools.
- Use structured cabling to save space.
5. Tree Topology Issues
Tree topology combines Star and Bus but has hierarchy risks.
Common Problems:
Here are some common problems.
- Root Node Failure – Breaks the whole network.
- High Cabling Requirement – Uses more wiring.
- Complex Troubleshooting – Faults at the top affect all.
- Scalability Challenges – Expansion increases load.
Solutions:
Here are some common solutions.
- Use redundant backbone devices.
- Optimize cabling with proper design.
- Apply diagnostic monitoring tools.
- Use high-capacity switches for scaling.
6. Hybrid Topology Issues
A hybrid is flexible but costly and harder to manage.
Common Problems:
Here are some common problems.
- Expensive Setup – Needs more resources.
- Complex Management – Multiple topologies = harder control.
- Troubleshooting Challenges – Time-consuming fault finding.
- Inconsistent Performance – Different speeds across sections.
Solutions:
Here are some common solutions.
- Plan the budget before implementation.
- Use centralized management software.
- Employ skilled IT staff.
- Standardize hardware for uniform performance.
Real Life Examples of LAN Topologies
LAN topologies are used differently depending on the place and purpose. Here are some real-life examples:
- Schools: Utilize a star topology for simplified management.
- Large Businesses: Opt for a hybrid topology for enhanced flexibility.
- Homes: Prefer star topology with Wi-Fi routers for ease and low cost.
- Hospitals/Universities: Often use mesh topology for high reliability.
Quick Comparison of LAN Topologies
Here’s an easy guide to see the cost, reliability, and best use for each LAN topology at a glance.
| Topology | Cost | Reliability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Star | Medium | High | Small offices, homes |
| Bus | Low | Low | Small networks with few devices |
| Ring | Medium | Medium | Networks needing organized data flow |
| Mesh | High | Very High | Large networks, hospitals, critical systems |
| Tree | Medium-High | High | Large organizations, universities |
| Hybrid | High | High | Big complex networks, flexible setups |
Conclusion
In this article, in this article, we’ve covered LAN topologies in detail. Each LAN topology has its own pros and cons, so always choose the one that fits your needs. For beginners, star topology is simple and reliable, while a hybrid is best for bigger networks. Be careful not to overload your central devices, as it may cause failures. A well-planned LAN topology not only improves speed but also makes your network secure and reliable.
Remember, the right LAN topology saves time, cost, and effort. Keep exploring, keep learning, and build a network that is fast, secure, and future-ready.
FAQs
Here are some common FAQs to help you understand LAN topology better.
LAN topology is the way computers and devices are arranged in a local area network. It defines how data moves from one device to another and shows the overall structure of the network.
LAN topology decides how fast and reliably data travels between devices. A good design reduces delays and prevents traffic jams. Poor topology may slow down the whole network.
Yes, it’s possible to combine topologies like star and bus. This is called a hybrid topology. It helps balance cost, performance, and flexibility.
Star topology is simple, easy to set up, and troubleshooting is faster. If one device fails, it doesn’t crash the whole network. That’s why most offices and homes prefer it.
The whole network goes down because all devices depend on the central hub or switch. This is the main drawback of star topology. Using a strong central device reduces this risk.
Yes, mesh is usually used in big networks because it needs many cables and devices. It offers high reliability since every device has multiple paths. Small networks rarely use it due to cost.
It depends on your budget, number of devices, and performance needs. Star is good for small to medium setups. Mesh works best for critical systems needing zero downtime.
Yes, some topologies are more secure than others. For example, in a star topology, securing the central hub adds strong protection. In a bus topology, A single point of failure can expose the whole network.
In ring topology, data passes through each device before reaching the target. More devices mean longer travel time. That’s why it’s slower and less used today.
Check the main cable first, since one fault can affect all devices. Loose connections and cable breaks are common problems. Using terminators properly helps avoid errors.
Yes, but often in mixed forms like hybrid topologies. Most modern LANs use a star as the base. Other types are used depending on need and budget.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks