Effective Types of Cloud Computing You Can Trust
Published: 30 Aug 2025
Types of Cloud Computing change the way we use business and individual technology every day. From storing images to running powerful business applications, Cloud Computing has become an integral part of our lives, even without our awareness. But here is the confusing part: do you know that there are different types of cloud computing, each is a unique purpose? Many people hear conditions such as public clouds, private clouds, and hybrid clouds, but struggle to understand what they really mean. With simple words, each type of Sky provides its own benefits, challenges, and use cases.

If you have ever thought about which cloud option may be right for your business, study, or even personal use, this guide will easily break it down for you.
🌥 What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the use Internet to store, manage, and process data instead of relying on your personal computer or office media. With simple words, it means using other people’s powerful computers (cloud) to run apps, save files, or access services online.
- Instead of saving everything on your device, you can access it anywhere with an internet connection.
- Examples include Google Drive, Dropbox, Microsoft 365, and Netflix, all of which are run on Cloud Computing.
- This makes technology cheaper, faster, and more flexible for both businesses and individuals.
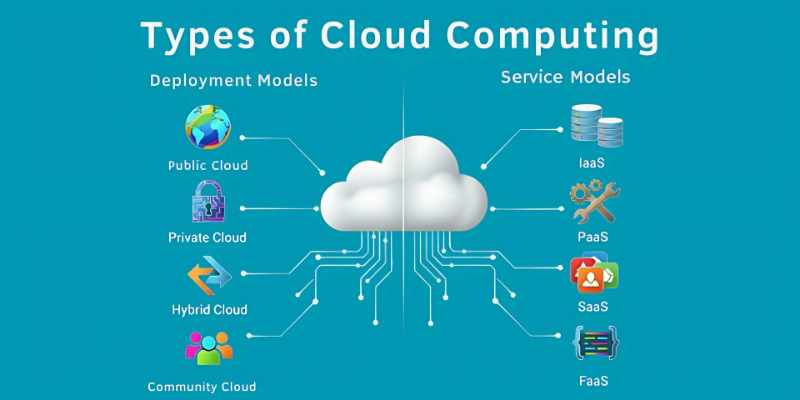
☁️ Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing comes in different types, each designed to meet specific business and user needs. Here is the list of some important Types of Cloud Computing.
Based on Deployment Models
These explain how cloud environments are set up and
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Community Cloud
Based on Service Models
These are ways cloud services are delivered to businesses and users
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
- FaaS (Function as a Service / Serverless)
Let’s explain these Types of Cloud Computing one by one.
Based on Deployment Models🏗️
Deployment models in cloud computing explain how cloud services are set up and delivered to users, depending on business needs and control
1. ☁ Public clouds
Public Cloud is like renting online space where many users share similar resources. Companies such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure manage everything.
- It is not necessary to buy or maintain hardware.
- Just pay for what you use (cost-effectiveness).
- Easy to use, quick, and easy to stand.
- Excessive scalable as your business grows.
- Available from the Internet.
- Great for startups and small businesses.
- Smaller pre costs compared to a private setup.
2. 🏠 Private clouds
Private clouds are only designed for a company, which provides more control and protection.
- Dedicated resources were not shared with others.
- Strong security and privacy for sensitive data.
- It may be hosted on the site or through a supplier.
- Suitable for banks, authorities, or health care.
- High costs, but more reliable for large companies.
- Adaptable to business requirements.
- Better compliance with industry rules.
3. 🔄 Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Clouds mix public and private clouds to get the best of both.
- Save public sensitive data, and less important data from the public.
- Saves money by keeping security strong.
- Flexible to handle the changing charge.
- Easy to scale under high demand.
- Reduces shutdown in many environments.
- Great for businesses growing rapidly.
- The remaining costs, performance, and security.
4. 🌍 Multi cloud
Multi-cloud means using more than one supplier (eg, AWS + Google Cloud).
- Avoids being dependent on a supplier.
- Improves reliability if a service fails.
- You choose the best features from different suppliers.
- Increases flexibility for businesses all over the world.
- Can reduce the cost of comparing suppliers.
- The seller helps avoid locking up.
- Perfect for global organizations with different needs.
Based on Service Models⚙️
Service models in cloud computing describe the different ways cloud services are offered to users, based on what they manage and what the provider handles
1. 🖥️ Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IAAS offers virtual machines, storage, and networks so that companies do not require physical hardware.
- Pay-as-you-go model (no major pre-investment).
- Scalable storage or serve at any time.
- Great for startups and growing businesses.
- Provides complete control over the operating system and apps.
- Reduces the cost of maintaining servers on-site.
- Flexible for test and development environments.
- Example: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure.
2. ⚙ Stage as a service (PAA)
PAA provides tools and platforms for developers to create apps without a server.
- Developers can focus on coding, not on infrastructure.
- It is ready to use and provides software frameworks.
- The app saves time in development.
- Automatically scales with use.
- Price efficiency for software teams.
- Simple collaboration for distance developers.
- Example: Google App Engine, Haroku.
3. Software as a service (Saas)
Software as a service (Saas) offers software applications on the Internet; no download is required.
- Available anywhere with an internet connection.
- It is not necessary to install or update the software.
- Cheap member-based prices.
- Great for individuals and businesses of all sizes.
- Light scales as layers grow.
- Provides real-time support.
- Example: Gmail, Zoom, Microsoft 365.
4. ☁ FaaS (Function as a Service / Serverless)
Faas lets you run the code without control of the server – it works automatically when released.
- Pay only for the exact time to run the code.
- Developers do not worry about server administration.
- Ideal for miniature, phenomenally operated tasks.
- Immediate scales with demand.
- Saves money by avoiding idle server costs.
- Great for apps like chatbots or notifications.
- Examples: AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions.
Real Life Examples of Cloud Computing 🌟
Real-life examples of cloud computing show how we use it every day in business, education, and even personal life, without always noticing
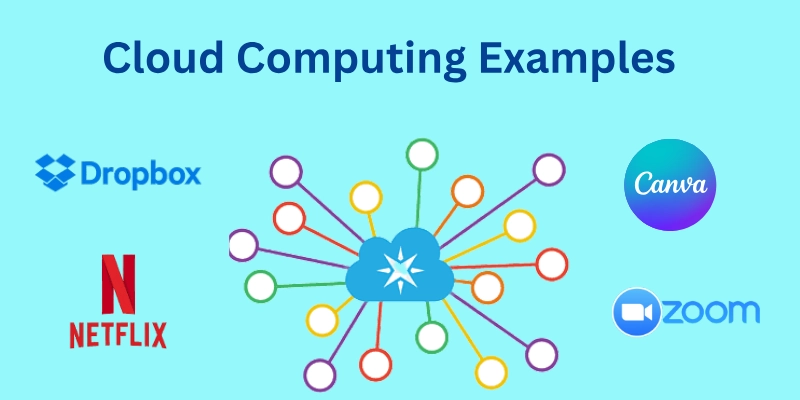
- Netflix: Uses cloud to stream movies worldwide.
- Dropbox: Stores and shares files easily.
- Zoom: Runs meetings using cloud servers.
- Canva: Lets you design online without downloads.
Conclusion
The Types of Cloud Computing give us flexible options to manage technology without storing data, running apps, and relying on individual devices. Whether it is a public cloud for startups, a private cloud for secure industries, or mixed with a hybrid cloud, each model has its own strengths. Service models such as IAAS, PA, Saas, and FaaS also make it easy to choose the level of control and convenience for companies and individuals, as they need.
The key is simple: Choose the right Types of Cloud computing that match your goals, budget, and security requirements. With the right choice, Cloud Computing can save money, improve speed, and open doors for smarter technology in everyday life.
FAQS
Here are the most important FAQs related to Types of Cloud Computing.
The main types include Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, and Community Cloud, along with service models like IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and FaaS.
Most small businesses choose the Public Cloud because it’s cost-effective, quick to set up, and easy to scale as they grow.
- Public Cloud is shared by many users and managed by providers like AWS or Google Cloud.
- Private Cloud is dedicated to one company, offering more control and security.
- IaaS: Rent IT resources like servers and storage.
- PaaS: A platform to build and run apps without managing hardware.
- SaaS: Ready-to-use software like Gmail or Zoom.
Hybrid Cloud combines Public and Private Clouds. It’s useful for companies that need both flexibility and strong security.
Yes! Every time you use Google Drive, Netflix, Dropbox, or iCloud, you’re already using cloud computing.
Community Cloud is shared by organizations with similar needs, like hospitals, schools, or government agencies. It offers security with shared costs.
It depends on your needs:
- For affordability, go with Public Cloud.
- For security, choose Private Cloud.
- For a mix of both, try Hybrid Cloud.
- For shared industries, use Community Cloud.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks